Boom and bust: Simulating the effects of climate change on the population dynamics of a global invader near the edge of its native range
Abstract
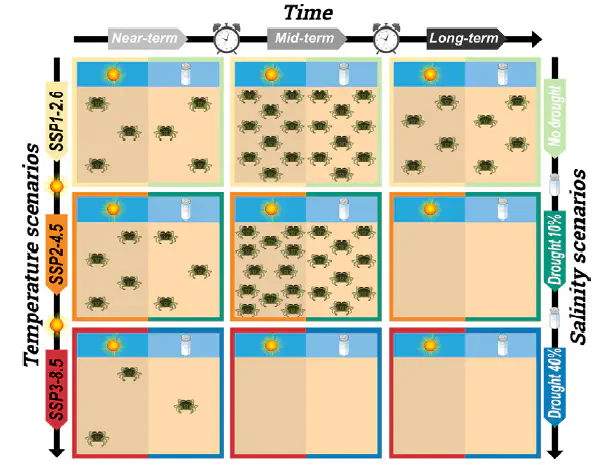
Despite the increasing awareness of climate change, few studies have used the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) scenarios to simulate the effects of climate change on estuarine populations of crustaceans. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of temperature and salinity fluctuations on the population dynamics of the shore crab Carcinus maenas at the southern edge of its native range. To this end, a population dynamics model was developed based on experimental and literature data on the biology, ecology and physiology of the species. Results showed that the shore crab will be more affected by changes in temperature than in salinity. The parameter sensitivity analysis revealed that the larval phase of the species is the most sensitive stage of the shore crab life cycle. Three IPCC scenarios (SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5, and SSP3-8.5) were used to simulate the effects of temperature increase on the population of C. maenas in the near- (2040), mid- (2060), and long-term (2100). Two scenarios of drought conditions accompanied by the estimated salinity change were also simulated (10 % and 40 % drought). Results suggested that slight increases in temperature (up to 2 °C) lead to a strong increase on the density of C. maenas in the midterm, while further temperature increases lead to a decline or local extinction of the shore crab population at the southern edge of its distribution range. Results indicated that a salinity increase in the estuary had a negative effect on the shore crab population. Given the importance of the species to temperate coastal ecosystems, both population increase and local extinction are likely to have significant impacts on estuarine communities and food webs, with unknown ecological and socioeconomic consequences.